Phase 3: IT strategic planning
Develop IT balanced scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a management system that clarifies the strategy and vision of an organization, translating them into action that can be tracked. It’s a way of understanding the performance of the department or entire organization – an alternate, or preferred, way to measure successful strategy implementation that goes beyond financials. In addition, a BSC is helpful in the prioritization of measurements that are most meaningful to the organization.
The original Balanced Scorecard defined four perspectives that help managers plan, implement, and achieve the business strategy:
- Financial Perspective: tracking financial requirements and performance
- Internal Business Process Perspective: measuring critical-to-customer process requirements
- Customer Perspective: measuring the satisfaction and performance requirements of customers, as it applies to both the organization and what it delivers (products or services)
- Knowledge, Education, and Growth Perspective: measuring how the organization educates employees, gains and captures knowledges, and uses this information to grow and stay competitive
To maintain a BSC, all four areas must be evaluated consistently. To delay examination or ignore a metric entirely will lead to an unbalanced business situation with inevitable and significant negative impact.
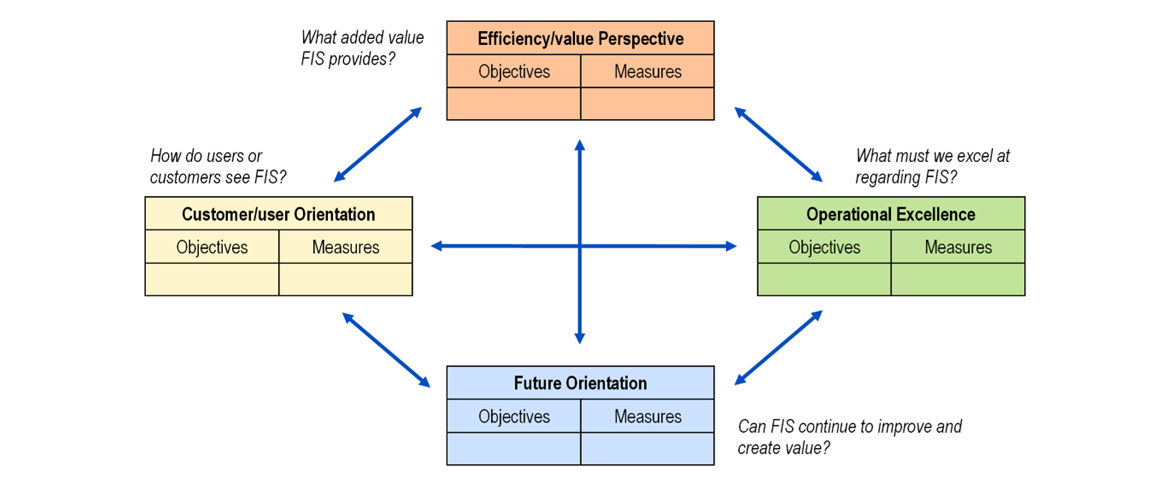
The BSC concept has been successfully employed in software engineering and IT projects. The traditional BSC was adopted in various ways to better fit an IT environment. Van Grembergen modified the four perspectives as follows:
- Corporate contribution.
- Customer (User) Orientation.
- Operational Excellence.
- Future Orientation.
A more general approach could be suitable also to the public sector - see figure below.