Phase 3: IT strategic planning
Define key performance indicators
Objective of the exercise
The objective of this exercise is to design and develop specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) key performance indicators (KPIs) in line with the related IT objectives to assess the FIS alignment against the objectives and the FIS efficiency criteria and thus, enable corrective action if needed.
Introduction
What are KPIs?
KPIs are a measurable value or metric to assess the performance and progress of an individual, team, department, or organization in achieving specific objectives or goals. KPIs are crucial in business and management as they provide a quantifiable way to track performance and ensure that efforts align with strategic objectives.
Key Performance Indicators are typically chosen based on their relevance to the organization’s overall mission and objectives. They should be SMART to be effective in providing meaningful insights and driving improvements.
Examples of KPIs can vary widely depending on the nature of the organization and its goals. Some common KPIs in different functional contexts include:
- Sales: Revenue, sales growth rate, customer acquisition rate;
- Customer Service: Customer satisfaction score, average response time, customer retention rate;
- Marketing: Conversion rate, website traffic, cost per lead;
- Finance: Profit margin, return on investment (ROI), cash flow;
- Human Resources: Employee turnover rate, employee engagement score, training completion rate;
- Manufacturing: Production efficiency, defect rate, on-time delivery.
By regularly monitoring and analysing KPIs, businesses can make data-driven decisions, identify areas for improvement and focus their efforts on achieving success in line with their strategic objectives.
What is the purpose of defining KPIs in developing FIS?
It should be remembered that the business objectives for building/improving a forest information system, and the corresponding IT-related objectives, have resulted from the analysis of what interventions could improve efficiency of the forest sector value chain (Phase 1). Tools are needed to assess the results of implementation of these strategies and, if necessary, to take corrective action. KPIs provide the necessary metrics for this purpose.
How FIS KPIs should be defined?
For each improvement strategy (linked to the business objectives), KPIs should be defined, as well as the means to assess them.
For example, for the business objective on “having control on illegal logging and deforestation”, and the corresponding IT objective on “creating a timber-tracking system”, the KPI could be: “the share of timber produced in the country which is tracked by the timber-tracking system”, or: “the number of forest inspectorates which have implemented the timber-tracking system”.
The KPIs must be SMART. They must provide the means for measuring the goals reached and the efficiency of critical processes linked to relevant business objectives. Potential KPIs could cover the following categories, with specifications:
Data accuracy: Measure the accuracy and reliability of the data stored and managed within the FIS via data validation rates of logic checks.
Data Timeliness: Measuring the timeliness of data updates and availability in the FIS.
System Performance: Assessing the performance and responsiveness of the FIS by including metrics on data and analysis processing.
System utilization and user satisfaction: Evaluating the extent to which the FIS is utilized (for example the number of administrative cases done using the FIS) and the level of satisfaction by stakeholders.
Decision-making support: Assessing the effectiveness of the FIS in supporting informed decision-making by tracking the number of decisions influenced by the system’s outputs.
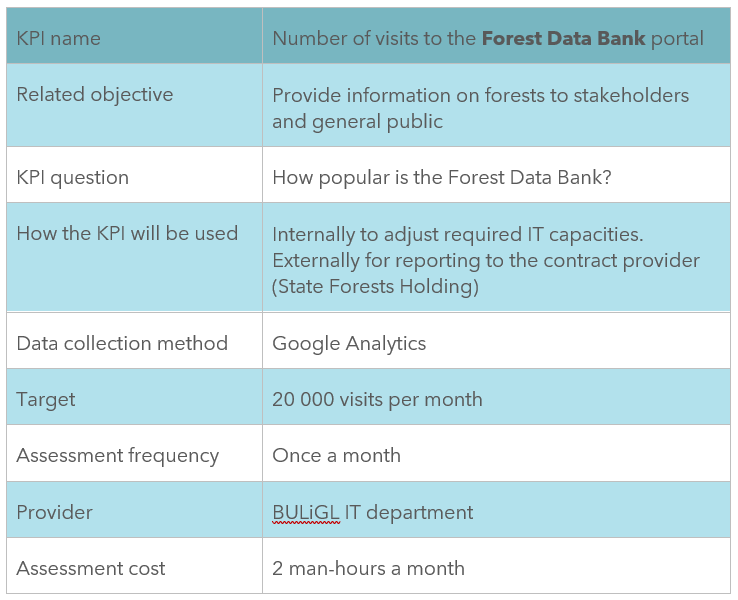
Step 1. Identification of KPIs
Identification of KPIs involves only 1 step. There are many approaches to defining KPIs. They depend on the context, organizational structure, objectives and level of the analysis/assessment. An example of a KPI developed for the Forest Data Bank in Poland is shown in Figure